October 10,2016. Monday
What is System Development?
•System is a set of components that interact to achieve a common
goal.
•Information system is a collection of hardware, software,
data, people and procedures that work together to produce information.
•System development activities are grouped into phases,
sometimes is called the system development life cycle (SDLC).
•System development should follow three general guidelines:
-Group activities or tasks into phases
-Involve users
-Define standards
• System development should involve representatives from each department in which the proposed system will be used
•Project management is the process of planning, scheduling, and then controlling the activities during system development.
•To plan and schedule a project efficiently, the project leader identifies:
-Project scope
-Required activities
-Time estimates for each activity
-Cost estimates for each activity
-Order of activities
-Activities that can take place at the same time
• A popular tool used to plan and schedule the time relationships among project activities is a Gantt chart
• A PERT chart also can be used for planning and scheduling time
•Feasibility is a measure of how suitable the development of a system will be to the organization:
-Operational feasibility
-Schedule feasibility
-Technical feasibility
-Economic feasibility
• Documentation is the collection and summarization of data and information
-A project notebook contains all documentation for a single project
• Users and IT professionals refer to existing documentation when working with and modifying current systems
•During system development, members of the project team gather data and information using several techniques
-Review documentation
-Observe
-Survey
-Interview
-JAD Sessions
-Research
Who Initiates a System Development Project?
•A user may request a new or modified system
•Organizations may want to improve hardware, software, or other technology
•Situations beyond an organization’s control might require a change
•Management might mandate a change
•A user may request a new or modified information system using a request for system services or a project request
Planning Phase
•The planning phase for a project begins when the steering commitee receives a project request
•Four major activities are performed:
-Review and approve the project requests
-Prioritize the project requests
-Allocate resources
-Form a project development team
Analysis Phase
•The analysis phase consists of two major activities:
1.Conduct a preliminary investigation
-Determines and defines the exact nature of the problem or improvement
-Interview the user who submitted the request
2.Perform detailed analysis
-Study how the current system works
-Determine the user' wants, needs, and requirements
-Recommend a solution
•Process modeling (structured analysis and design) is an analysis and design technique that describes processes that transform inputs into outputs
-Entity-relationship diagrams
-Data flow diagrams
-Project dictionary
• An entity-relationship diagram (ERD) is a tool that graphically shows the connections among entities in a system
• Entities are objects in the system that have data
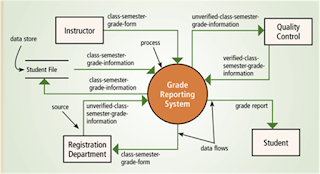
• A data flow diagram (DFD) is a tool that graphically shows the flow of data in a system
-Data flows
-Processes
-Data stores
-Sources
• The project dictionary contains all the documentation and deliverables of a project
• Structured English is a style of writing that describes the steps in a process
•A decision table is a table that lists a variety of conditions and the actions that correspond to each condition
•A decision tree also shows conditions and actions, but it shows them graphically
• The data dictionary stores the data item’s name, description, and other details about each data item
•Objectmodeling combines the data with the processes that act on that data into a single unit, called an object.
•UML(Unified Modeling Language)has been adopted as a standard notation for object modeling and development
-UML includes 13 different diagrams
-Two diagrams include:
-Use case diagram
-Class diagram
• A use case diagram graphically shows how actors (users) interact with the information system
• Diagrams are considered easy to understand
• A class diagram graphically shows classes and subclasses in a system
• Each class can have one or more subclasses
• Subclasses use inheritance to inherit methods and attributes of higher levels
•The system proposal assesses the feasibility of each alternative solution
•The steering committee discusses the system proposal and decides which alternative to pursue
-Packaged software
-Custom software
-Outsourcing
Design Phase
•The design phase consists of two major activities:
-Acquire hardware and software
-Develop all of the details of the new or modified information system
• To acquire the necessary hardware and software:
•The next step is to develop detailed design specifications
-Sometimes called a physical design:
-database design
-Input and output design
-Program design
• Systems analysts typically develop two types of designs for each input and output
• A prototype (proof of concept) is a working model of the proposed system
-Prototypes have inadequate or missing documentation
-Users tend to embrace the prototype as a final system
-Should not eliminate or replace activities
•Computer-aided software engineering(CASE)tools are designed to support one or more activities of system development
•CASE tools sometimes contain the following tools:
-Project repository
-Graphics
-Prototyping
-Quality assurance
-Code generator
-Housekeeping
• Many people should review the detailed design specifications
• An inspection is a formal review of any system development deliverable
– A team examines the deliverables to identify errors
Implementation Phase
•The purpose of the implementation phase is to construct the new or modified system and then deliver it
-Develop programs
-Install and test the new system
-Train users
-Convert to the new system
•The program development life cycle follows these steps:
-Analyze the requirements
-Design the solution
-Validate the design
-Implement the design
-Test the solution
-Document the solution
•Various tests should be performed on the new system
1.Unit test
-Verifies that each individual program or object works by itself
2.Systems test
-Verifies that all programs in an application work together properly
3.Integration test
-Verifies that an application works with other applications
4.Acceptance test
-Checks the new system to ensure that it works with actual data
• Training involves showing users exactly how they will use the new hardware and software in the system
– One-on-one sessions
– Classroom-style lectures
– Web-based training
• One or more of four conversion strategies can be used to change from the old system to the new system
Operation, Support, and Security Phase
•The purpose of the operation, support, and security phase is to provide ongoing assistance for an information system and its users after the system is implemented
-Perform maintenance activities > Monitor system performance > Assess system security
•A computer security plan should do the following:
-Identify all information assets of an organization
-Identify all security risks that may cause an information asset loss
-For each risk, identify the safeguards that exist to detect, prevent, and recover from a loss.
















No comments:
Post a Comment